Every gardener who grows watermelons in his area has at least once encountered diseases and pests of melons. They can cause great damage to the crop, so you should carefully study the methods of combating diseases and insects.
Watermelon Disease
Various diseases of watermelons significantly reduce the yield. Some may even leave the gardener without fruit at the seedling stage. Therefore, it is important to constantly monitor the plants and know how to save them when identifying doubtful signs.
Fusarium
This disease is caused by a fungus that penetrates the root system of gourds. First, small orange spots appear on the roots, which are tightened with a light pink coating. As the disease develops, the roots become dark, the base of the stem rots, the foliage turns yellow, dries and falls. The bush weakens and stops growing.

Fusarium - one of the most harmful and common fungal diseases of watermelons
It is impossible to detect fusarium at an early stage, since the plants are affected from the roots. When the external signs of the disease are visible on the watermelon, it means that it has already been started and cannot be treated. It remains only to remove diseased bushes and treat the soil with a solution of copper sulfate. And the rest of the plants are sprayed for prevention with fungicides.
I heard from my grandmother, who grew watermelons all her life, that the reason for the fusarium withering of melons is overmoistening of the soil and cooling of the soil to 16-18aboutC. Therefore, I am now very diligently caring for watermelons to avoid diseases. And for prevention after harvesting, you should remove from the site and destroy the dried parts of the wattle fence and disinfect the soil.
Anthracnose
The causative agent of the disease is a fungus. It manifests itself in blurry yellow and brown spots on the leaves. Later they enlarge and become covered with yellow-pinkish pads. Later, spots turn into dark ulcers that spread to the stems and fruits. Leaves dry, watermelons are deformed, cease to grow and rot.

Anthracnose especially affects watermelons in rainy weather.
Anthracnose can be cured by spraying the plant with a 1% solution of Bordeaux fluid (1 g of active substances per 100 ml of water). The bush should be treated evenly: the drug acts only where it got. The procedure is carried out three times with an interval of 7-10 days. You can use fungicides (Tsineb, Kuprozan) according to the instructions. The soil must be disinfected with a 2% solution of potassium permanganate (2 g of the substance per 100 ml of water) or copper sulfate (1 tbsp. L. Of the drug per 10 l of water). For 1 bush, 1.5 l of solution is enough. The soil is shed around the plant once. Careful weeding and removal of affected leaves and stems is also required.
From the first episode of manifestation of anthracnose, it became clear that this disease is dangerous for watermelons, as it can destroy plants completely. We did not identify the pathology on time and the fungicides did not help save the crop. Therefore, it was necessary to tear out the affected plants and burn them. Now we try to comply with preventive measures: we soak the seeds in Skor, Tiram or Ridomil Gold and process the bushes with Kuproksat three times a season.

Cuproxate is a prophylactic contact fungicide designed to protect fruit and vegetable crops.
Root rot
The cause of infection with this fungal disease can be a strong temperature difference, humidity, hard watering with soil solutions. Signs of root rot are weeping black-brown spots at the bottom of the stem and on the shoots. The roots become thicker, crack, and their surface breaks up into threads. Leaves turn yellow, wither, the plant dies.

Root rot first affects the roots, and then the rest of the plant
You can treat the disease only at the very beginning of its appearance, at the advanced stage, the bushes need to be destroyed. Watering must be reduced, and water replaced with a pink solution of potassium permanganate. The roots are removed from the soil and treated with copper sulfate and wood ash (8 g and 20 g, respectively, to 0.5 l of water). After some time, watermelons are treated with drugs that contain metalaxyl or mefenoxam. Spraying is necessary 3-4 times every 2 weeks.
We were lucky: our watermelons did not have root rot. But the neighbors in the plot lost more than half of the harvest. To prevent rot, the seeds should be decontaminated before planting in a 0.025% solution of iron sulfate, copper sulfate or in a 1% solution of potassium permanganate. And it is advisable to sprinkle the root neck every week with crushed chalk and spray the bushes with a 0.1% Fundazole solution.
You can not use fertilizers that contain chlorine: because of them, the roots of the watermelon weaken.
Bacterial spotting
This ailment is caused by bacteria that insects can bring on melon. They breed at temperatures above 30aboutC and humidity 70%. Signs of spotting are watery spots with a green-yellow edging. Later they become larger, merge, the leaves turn black, the bush dies. Dark rounded growths are noticeable on watermelons.

There are no preparations for treating watermelons for bacterial spotting, infected bushes must be destroyed
At the beginning of the disease, the bush can be saved. To do this, cut off all leaves that have even slight signs of damage. It is recommended to capture a healthy part of the leaf (0.5 cm). After each cut, the knife must be treated with alcohol. If such procedures do not give any result, then the plant is destroyed. The soil must be sanitized.
Before I started practicing watermelons, I had to study a lot of literature on the cultivation of melons. I paid special attention to disease prevention, as I know that it is easier to prevent a disease than to treat it later. Therefore, the seeds are planted before planting in a solution of Fitosporin, I disinfect the soil for seedlings with Trichopolum (1 tablet in 2 liters of water). And in the summer, I spray the bushes with Gamair (every 20 days).
Powdery mildew
If on the leaves, fruit ovaries white spots are visible with a plaque similar to flour, then the culture is infected with powdery mildew. This disease also causes fungus. Over time, the coating becomes brown, dense, and a cloudy liquid is released from the spots. The infected parts of the bush turn yellow. The fruits are deformed and rot.

Powdery mildew spreads quickly during cool and damp weather
If powdery mildew symptoms are found, urgently need to process the bushes using a 25% suspension of Caratan. Topaz, Planriz, Bayleton have also proved themselves well. Before processing, cut and burn the infected parts of the watermelon.

Topaz is a highly effective systemic fungicide that protects crops from many fungal diseases.
Video: powdery mildew prevention and control measures
Downy mildew
This is a fungal disease. The leaves on the front side are covered with rounded oily spots of light yellow color. And from below, a gray-purple coating forms on them. Leaves frown, dry out. The fruits cease to grow, mutate, become tasteless, the flesh loses its color.

The development of downy mildew is promoted by high humidity, sudden changes in temperature, fog, cold dew, watering plants with cold water, and in the greenhouses there is also condensation on the film or glass
Having noticed the first signs, it is necessary to treat the bushes with a solution of colloidal sulfur (70 g per bucket of water). The same means should be watered and the soil. If the signs of the disease have not disappeared, then apply Strobi, Polycarbacin, Quadris.
There are often fogs in our region. Therefore, downy mildew is a common occurrence. To prevent it, I lower the seeds of watermelon before planting for a quarter of an hour in hot water (50aboutFROM). And also once a month I water the garden with Fitosporin (I make the concentration of the drug 2 times less than indicated in the instructions).
White rot
Sclerotinia sclerotiorum is a fungus that causes the formation of the disease. It spreads in cold weather and in high humidity. The lower leaves become watery, translucent. A whitish coating similar to cotton wool is noticeable on them. Later it becomes dense and dark. The top of the bush wilts, shoots soften, rot.

If most of the bush is infected with white rot, then the plant must be destroyed
Having discovered the disease, all infected parts of the bush are cut with a sharp disinfected knife. Slices should be sprinkled with colloidal sulfur or activated carbon. Plants are treated thrice with an interval of 7 days with fungicides (Topaz, Acrobat MC).
Gray rot
The fungus that causes this disease lives for several years in plant debris in the ground. But gray rot develops only under conditions suitable for it: in coolness and dampness. On watermelons, buds, leaves appearing dots of brown color, covered with a grayish coating with small dark dots.

Gray rot affects all parts of the plant: leaves, buds, fruits
If the disease is not started, then watermelons are saved by treatment with Teldor, Topaz, Sumileks. You can prepare the product from crushed chalk and a solution of copper sulfate (2: 1).
It is recommended to plant marigolds, leaf mustard, calendula around melon. These plants secrete phytoncides that kill the fungus.

Calendula not only decorates the site, but also saves watermelons from gray rot
In our family, to save the crop from gray rot, a solution is used: for 10 liters of water, 1 g of potassium sulfate, 10 g of urea and 2 g of copper sulfate. Only before spraying the plants should the diseased parts of the plant be removed.
Mosaic disease
This viral disease appears as bright patches on the leaves. Later, leaf plates are deformed, dry out, and the bush ceases to grow. On the fruits of the watermelon bloating, tubercles, mosaic coloring are observed.

Mosaic disease leads to a significant decrease in watermelon yield
This disease can be transmitted by pests, it is transmitted through seeds, infected tools. There are no drugs for the treatment of the virus yet. But with the timely detection of signs of the disease, you can apply Karbofos. Spray the plants 2 times with an interval of 1 week.
Leaf rust
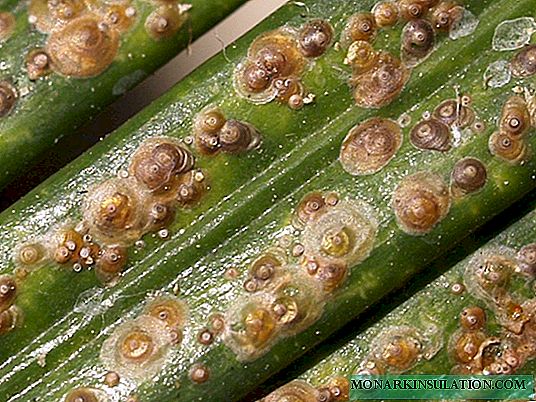
This disease is caused by rust mushrooms. The main symptom of the disease is the appearance on the bush of brown tubercles of various shapes and sizes. Later they crack and a rusty powder spills out of them - spores of the fungus. The disease develops due to high humidity or an excess of nitrogen fertilizers.

Rust causes the death of leaves, and in the case of severe damage - and other parts of the plant
The disease can be cured with the help of the fungicides Topaz, Strobi, Vectra, Bordeaux fluid. First you need to cut off the affected leaves and shoots.
Olive spotting
The disease causes a fungus. It does great harm to the fruit. Concave spots of olive-gray hue are visible on them, from which a cloudy liquid is released. Spotting is transmitted to leaves and stems, they become brittle. In 5-10 days, the bush can die completely.

Olive spotting affects all aerial parts of the plant.
Sources of olive blotch are plant debris, an infection in the soil that persists in it for up to 3 years.
If symptoms of the disease are detected, the bushes should be treated with 1% Bordeaux fluid. The advanced stage is treated with Oxychom, Abiga-Peak, treating watermelons three times with an interval of 1 week.
Disease Protection and Prevention
Watermelons are prone to many diseases that are easier to prevent than to cure. Therefore, every gardener who grows gourds on his plot should remember several important rules in order to protect his crop:
- The gardener must inspect the plants every day for uncharacteristic changes. In the early stages of the disease, it is easier to cure.
- Soil before sowing seeds must be disinfected. It is steamed, kept in the freezer, calcined in the oven.
- Watermelon seeds should be decontaminated with a 1% potassium permanganate solution.

The treatment of seeds with potassium permanganate not only disinfects them, but also nourishes the necessary microelements for growth
- Be sure to remove plant debris from the site: pathogens can remain on them for several years.
- It is important to choose illuminated and well-ventilated areas for melon growth, where before that, gourds, pumpkin crops, and cucumbers were not grown for at least 3-4 years.
- Plants should be planted freely when planted. So bacteria cannot spread quickly.
- When growing watermelons, do not forget about regular cultivation. Do this after each watering or rain for better aeration of the root system.
- Top dressing is an important step in caring for watermelons.
Fertilizers provide plants with important macro- and microelements, and strong bushes are much less likely to suffer from diseases
- Watering the bushes is necessary under the root, avoiding moisture on the leaves. Water should be at room temperature.
- It is important to carry out preventive treatments with fungicides that protect plants from a wide range of fungal and infectious diseases.
Video: watermelon disease prevention
Watermelon Pests
Watermelons can not only hurt, but also be affected by pests. Most of them carry pathogens, so they need to be fought.
Gourd aphids
Aphids are insects that settle on the inside of the leaf, flowers, watermelons, completely clinging to them. It is impossible not to notice them. The leaves are covered with a dark coating and drops of sticky liquid. Infected areas are deformed, dry out, the plant dies.

Melon aphids form large colonies on the underside of the leaf, but can be found on shoots, flowers, fruits
You can drive aphids folk remedies. Insects do not tolerate the pungent smell of infusions of onions, tobacco, garlic, citrus peels, and mustard powder. Processed bushes 2 times a week. If there are a lot of aphids, then any insecticides will help, for example, Inta-Vir, Commander, Mospilan. Watermelons are sprayed 4 times with an interval of 5-7 days.
It is advisable to use different drugs so that insects do not develop immunity.
Ladybugs are the worst enemies of aphids. Therefore, we plant spicy plants near the melon, the smell of which attracts them. You can also build bird feeders at the site. Titmouse, sparrows, linnet will fly and at the same time eat green insects.

Ladybug larvae can be purchased in specialized garden centers, and then released on their site
An American scientist calculated the total mass of aphids that parasitized on a 2-hectare site - it amounted to 25 kg.
Wireworm
The wireworm is the larva of the nutcracker. This pest gladly settles on the fruit and makes through holes in them. They begin to rot.

The wireman can be in the ground for 4 years
You can get rid of this pest using traps: jars are dug into the ground and pieces of potatoes and carrots are placed in them. Several times a week, baits must be replaced with fresh ones. In the aisles should be planted leaf mustard, beans: they scare the wireworm. And to destroy the trapped insects. If there are a lot of larvae, then the plants are treated with Provotox, Earth, Diazonin. These chemicals adversely affect the soil and crop, so they can only be used as a last resort.
Spider mite
On the underside of the sheet you can find dots of brown hue, the diameter of which is gradually increasing. The whole plant is entangled in a small transparent web. Later, the bush dries and dies.

The spider mite is so small that it can not be seen, but this pest causes a lot of damage to the plant
The spider mite is not an insect, so ordinary insecticides will not destroy it. To control the pest, acaricides are used: Neoron, Apollo, Actofit. Plants are treated 3-4 times with an interval of 5-10 days.
Acaricides are very toxic, so when working with them, remember about personal protective equipment.
Thrips
On the leaves of melons and gourds, small dark brown lines are noticeable - these are pests. They feed on plant juice. Infected areas become colorless, die off. The neglected stage is characterized by an unnatural silvery shade on the leaves, the stems mutate, the flowers fall off. Thrips is distributed in heat and in dry air.

Thrips are not only harmful to the plant, but also are carriers of pathogens of many dangerous diseases
Traps for these bugs are made of cardboard, covering its surface with honey, petroleum jelly or glue that dries for a long time. You can deal with pests and folk methods. Well help infusions of herbs:
- celandine
- garlic
- tomato tops
- green marigolds.
If the number of parasites increases, then the bushes should be treated with insecticide preparations:
- Karate,
- Spintor
- Fitovermom.
Use drugs 3-4 times with an interval of 1-2 weeks. Affected parts of the bush are removed.
Sprout fly
Watermelon pests are sprout fly larvae. They gnaw the stem and roots from the inside, the bushes begin to rot.

The eggs of a sprout fly winter in the soil, so it must be dug in the fall and loosened in the spring
It is recommended to fight larvae with the same drugs that are used to control aphids. Processing should not only the bush, but also the soil.
Gall nematode
This pest is a 1-2 cm round worm. Parasites develop at moderate soil moisture and a temperature of 20-30aboutC. They infect plant roots. The bush wilts, as if it lacks moisture and nutrients. The leaves curl, the watermelon stops growing and dies.

Nematode-affected plants have many filamentous roots called root beards.
Nematodes should be treated with chemicals, such as a 0.02% solution of mercaptophos or phosphamide. Processing is carried out 2-4 times with an interval of 3-5 days.
These drugs cannot destroy the eggs of the worms, since they have a strong shell. When chemicals lose their strength, the nematodes hatch.
Butterfly Scoops
Caterpillars of scoop butterflies are pests of gourds. They live in the ground, and at night they climb to the surface and begin to gnaw shoots, leaves of plants.

Young caterpillars feed on weeds first, and then switch to cultivated plants
Watermelons can be saved from caterpillars by spraying melon with the infusion of flowering wormwood: 300 g of raw materials, 1 tbsp. wood ash and 1 tbsp. l pour liquid soap 10 liters of boiling water and insist 5-6 hours. After cooling, the bushes are treated. Chemicals showed good results against caterpillars: Decis, Sherpa.
Locust
Locusts are another watermelon pest. These insects feed on all parts of the plants, and their larvae eat roots.

After the locust invasion, the melons become empty and lifeless
You can fight locusts mechanically if several individuals are found on the site. In a mass invasion, only chemicals will help: Taran, Karate Zeon.
Birds
Starlings, sparrows, crows, pigeons do not mind eating a delicious watermelon. Of course, they will not be able to completely destroy the crop, but they will ruin its presentation. And in the pecked areas, insect pests are often populated and bacteria penetrate.

On a field where watermelons are just starting to ripen, the crow will find exactly the ripe and juiciest berry
To protect gourds from birds, you can use plastic or textile nets. But they use this method only in small areas due to the high cost of the material. On limited areas, watermelons are protected with plastic (with holes) or wire boxes, which are installed above the fruits upside down.
Prevention of pests on melon
Prevention of pests is the same as disease: the removal of plant debris, the destruction of weeds, the observance of crop rotation. But there are other protective measures:
- The larvae of many pests winter in the soil, so in autumn and spring the site should be well dug.
- Mandatory stage - preventive treatment with insecticides. They are carried out after the appearance of sprouts and during flowering. Apply BI-58, Fitoverm.

Fitoverm - a broad-spectrum insecticide that protects watermelons from pests
- You can also spray young plants with infusion of onion husks (200 g per bucket of water).
- In the heat, watermelons are irrigated with clean water to prevent aphids from multiplying.
- Seeds are treated with Fentyuram.
- To destroy the wireworm, Bazudin is introduced into the soil before planting.
Summary table: problems with growing watermelons and their solution
| Problem | Possible reason | Decision |
| Leaves turn yellow at watermelons, seedlings |
|
|
| Dry, wither leaves or their tips |
|
|
| White spots on the leaves of seedlings | Sunburn. | Remove seedlings from the windowsill or pritenit so that direct sunlight does not fall. |
| Watermelons bloom |
|
|
| Stems are pulled on seedlings, leaves are smaller |
|
|
| Watermelons do not grow or grow poorly |
| Create watermelon appropriate conditions for growth. |
| Uneven shoots |
|
|
If there were problems when growing watermelons, pests attacked the plants or the bushes became ill, this does not mean that there will be no harvest. With the timely detection of a problem, compliance with the rules of treatment and prophylaxis, plants can be saved.